Mckinsey Job Aptitude Test
In the realm of top-tier consulting firms, few names resonate as strongly as McKinsey & Company. Known for their rigorous selection process, McKinsey’s aptitude test is a crucial step on the path to joining their esteemed ranks. In this blog post, we delve into the intricacies of the McKinsey Aptitude Test, providing insights and strategies to help you navigate this critical phase of your career journey.
What to expect (The Test Format)
Mckinsey Job Aptitude Test(developed by the in-house recruiting team) is mainly a problem-solving test. Your ability to read and interpret graphs and charts will be tested.
Your speed and accuracy in answering the questions are key to your success in the Job Aptitude test.
Why do I need Mckinsey Past Questions?
1. Insights into Test Format
McKinsey Past Questions offer a unique glimpse into the test’s format, structure, and the types of questions posed in previous assessments. By immersing yourself in these questions, you’ll become acquainted with the patterns, question styles, and cognitive skills that the test aims to evaluate. This familiarity can be a game-changer as you tailor your study plan to align with the specific demands of the test.
2. Realistic Test Simulation
One of the greatest advantages of practicing with McKinsey Past Questions is the ability to simulate the actual test experience. By adhering to time limits and navigating the questions under simulated test conditions, you’ll develop the poise and confidence needed to perform your best on the test day. This realistic simulation helps alleviate anxiety and ensures you’re well-prepared to face any challenges that arise during the actual assessment.
3. Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills
McKinsey Past Questions challenge your analytical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Regularly engaging with these questions sharpens your cognitive skills, helping you think critically, analyze complex scenarios, and arrive at well-structured solutions. Over time, this practice leads to an increase in your problem-solving speed and accuracy, essential attributes for success in the consulting field.
4. Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses
As you work through McKinsey Past Questions, you’ll gain a clearer understanding of your strengths and areas that need improvement. This self-assessment is invaluable as it guides your study efforts. You can dedicate more time to refining your weaker areas while reinforcing your strengths, ultimately fine-tuning your overall test performance.
5. Confidence Boost
Facing an assessment as significant as McKinsey’s can be daunting. However, as you progressively master McKinsey Past Questions, your confidence will naturally grow. You’ll enter the test room armed not only with knowledge but with the assurance that you’ve invested the time and effort to master the challenges that lie ahead.
Mckinsey Sample Questions and Answers.
Innovation Capital
The Group of Eight or G8 is a group comprised of political representatives of eight of the world’s largest eleven economies: United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, France, Italy, Japan and Russia. The G8 meet periodically to discuss issues of importance to member states and agree upon measures to address these issues.
The countries that comprise the G8 have been experiencing slow economic growth in recent years, and this is an important topic to be discussed at the next meeting of G8 Finance Ministers. In preparation for this meeting, a McKinsey team, working together with a group of external thought leaders and academics, are preparing a report on the importance of Innovation as a contributor to economic growth. The team intends to introduce a concept to the G8 representatives known as ‘Innovation Capital’, which is the value of all innovation-related assets which contribute to growth in productivity in the economy.
The team further defines three types of Innovation Capital:
- Physical Capital: Investments in information and communication
- Knowledge Capital: Investments that build the intellectual property and brand value of a company or organization
- Human Capital: Investments that build individual or group abilities and skills within companies or organizations
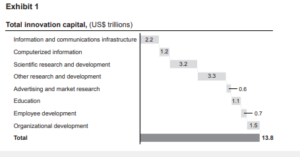
Exhibit 1 shows the main components of Innovation Capital and their total value across 16 countries that the team has been studying, including the members of the G8.
1. Which of the following MOST accurately describes the reason for the team’s work in preparing for the G8 meeting?
A. The team has discovered a new economic measure known as Innovation Capital and wants to introduce it
B. The team wants to explain how Innovation can drive economic growth
C. The team wants to explain how Innovation can represent a large proportion of an economy’s size
D. The team wants to convince the group to invest more in Innovation Capital in the future
Answer B
2. Which of the following analyses would be LEAST appropriate in better understanding the size of investments in Innovation Capital in the countries the team has been studying?
A. Analysis of expenditure by organizations on training programs for their employees
B. Analysis of expenditure by organizations on activities which build awareness of their aims and purpose
C. Analysis of expenditure by organizations on networking and socialization meetings and events
D. Analysis of expenditure by organizations on the management of their databases and information systems
Answer C
3. Which of the following can be concluded based on the information provided in Exhibit 1 regarding the countries being studied?
A. 45% of all Human Capital is invested in Organizational Development
B. 51% of all Innovation Capital is Knowledge Capital
C. More than 10% of Innovation Capital is invested in Computerized Information
D. More than a quarter of Innovation Capital is Scientific Research & Development
Answer A
4. If total Innovation Capital in Exhibit 1 were to grow by 5% per year in the future, which of the following would be the MINIMUM required annual growth in Human Capital that would see it represent more than half of total Innovation Capital in 10 years?
A. 10%
B. 15%
C. 20%
D. 25%
Answer B
The team proceeds to examine changes in business sector growth in a number of European countries in recent years, that is, the change in the total value of goods and services produced by the business sectors in these countries.
Growth in the value of goods and services can be driven by two factors:
- Hours: Changes in the total hours worked can drive changes in the total
goods and services produced. - Productivity: Even if the same number of hours have been worked, a more
or less productive workforce can generate greater or lesser goods and services.
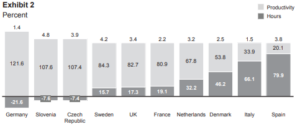
Exhibit 2 shows the average contribution of these two factors towards business sector growth in ten European countries over the last 12 years. Average annual business sector growth is given at the top of each bar. Within each bar, the light grey portion represents the proportion of this growth driven by changes in Productivity, while the dark grey portion represents the proportion of this growth driven by changes in Hours.
5. Which of the following statements, if true, would BEST explain why the information in Exhibit 2 is important for the team?
A. Most of the countries in Exhibit 2 have experienced negative economic growth in the last 2 years
B. In most countries, the business sector is the biggest contributor towards Innovation Capital
C. Growth in Hours is mostly driven by growth in the size of the working population
D. Growth in Productivity is mostly driven by growth in Innovation
Answer D
6.Which of the following statements is TRUE based on the information provided in Exhibit 2?
A. Hours grew by 24% across all ten countries over the last 12 years
B. Slovenia had the greatest growth in Productivity over the last 12 years
C. Spain had the least growth in Productivity over the last 12 years
D. Germany had the least growth in Hours over the last 12 years
Answer B
7. To the nearest tenth of a percentage point, what is the difference between Germany’s and Spain’s average annual business sector growth due to productivity over the last 12 years?
A. 0.1 percentage points
B. 0.5 percentage points
C. 0.9 percentage points
D. 1.3 percentage points
Answer C
8. Which of the following, if true, LEAST explains the data for Slovenia and Czech Republic in Exhibit 2?
A. Over the last 20 years, the average age of the population in these countries has been steadily increasing
B. Prior to the period in Exhibit 2, these countries were emerging from Communist economies with comparatively poor infrastructure and productivity
C. Net migration into these countries has been negative over the last 12 years
D. Changes in employment laws in these countries have led to greater flexibility for employers in setting working hours for their employees
Answer D
In preparing further for the G8 meeting, the team decides that it would be a good idea to use some specific examples of recent major innovations to help better explain the importance of Innovation Capital. A team member suggests using Apple’s iPod music player as such an example. The team readily agrees to this suggestion. They believe that the development of the iPod not only illustrates all three types of Innovation Capital, but it also shows how up-front investment in Innovation Capital can lead to follow-on advantages for the investor that accumulate over time.
9. Which of the following statements LEAST illustrates the Innovation Capital underlying the development of Apple’s iPod?
A. New software and technology was required to allow the distribution of music through online channels
B. New pricing was negotiated with the music industry to encourage online music purchasing
C. New design concepts were developed that gave the product an appealing look and feel
D. A new way of working with the music industry was developed to allow rapid distribution of new music to iPod users
Answer B
10. Which of the following analyses would BEST illustrate the team’s beliefs regarding Apple’s iPod?
A. An analysis of the market share achieved by Apple for its products subsequent to the iPod
B. An estimate of the size of the investment made by Apple in the development of the iPod
C. An estimate of the profit margins of the music industry subsequent to the launch of the iPod
D. An analysis of the reactions of technology experts to the iPod and subsequent Apple products
Answer A
Marcadia
Marcadia is an online store which offers a wide range of goods to customers via mail order. Marcadia has been in existence for five years and has seen rapid growth in sales during this period, as more and more new customers signed up. However, recently Marcadia’s customer numbers have plateaued and this has resulted in slower sales and profit growth.
The Managing Director of Marcadia has engaged McKinsey to help her better understand the purchasing behavior of her customers. She believes that a better understanding of customer purchasing can lead to more targeted and successful marketing. She tells the team: ‘I’m sure that our most valuable customers have certain purchasing behaviors that we can identify. If we can encourage more of our customers to adopt those behaviors, we can make them more valuable to us and this can inject a new source of growth into our business.’
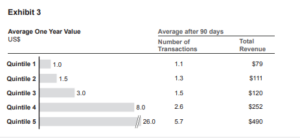
Exhibit 3 shows some data which the team has collected regarding a sample of 500,000 Marcadia customers who signed up in the last calendar year.
The customers are split into quintiles according to their one year customer value, from lowest to highest. ‘One year customer value’ is defined as the profit made by Marcadia on purchases made by a customer in their first year since signing up. Also presented is data on purchasing by customers in each quintile in their first 90 days since signing up, namely the average number of purchase transactions and the total revenue received by Marcadia from those transactions.
11. Which of the following statements BEST describes why the Managing Director of Marcadia has engaged McKinsey?
A. She believes that Marcadia can become better at identifying customers who stop making purchases
B. She believes that Marcadia can become better at identifying ways to encourage customers to spend more
C. She believes that, by focusing on the customers of greatest value, Marcadia can drive renewed growth in their business
D. She believes that Marcadia can predict the purchasing behavior of its
customers better
Answer B
12. Which of the following CANNOT be concluded from the information presented in Exhibit 3 regarding the sample of customers analyzed?
A. Purchasing by customers in their first 90 days is an indicator of their value to Marcadia in their first year
B. Quintile 1 are the customers with the lowest profit margin for Marcadia
C. The average customer makes between 2 and 3 transactions in the first 90 days since signing up
D. The average one year customer value is $7.90
Answer B
13. What is the correct ranking of the five quintiles in Exhibit 3 according to the average transaction revenue, from lowest to highest?
A. 1, 2, 4, 3, 5
B. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
C. 1, 3, 2, 4, 5
D. 1, 3, 2, 5, 4
Answer D
14. If Marcadia had driven higher purchasing from the new customers in Exhibit 3 so that the one year value of customers in Quintiles 1 thru 4 were each to increase to the next highest quintile, how much greater would Marcadia’s total one year customer value have been?
A. $250,000
B. $650,000
C. $2.5 million
D. $6.5 million
Answer C
About Mckinsey & Company
McKinsey & Company is a global management consulting firm founded in 1926 by University of Chicago professor James O. McKinsey, that offers professional services to corporations, governments, and other organizations. McKinsey is the oldest and largest of the “Big Three” management consultancies (MBB), the world’s most prestigious strategy consulting firms. The firm mainly focuses on the finances and operations of their clients.
McKinsey has a notoriously competitive hiring process and is widely seen as one of the most selective employers in the world. McKinsey recruits primarily from the world’s top business schools and was one of the first management consultancies to recruit a limited number of candidates with advanced academic degrees (e.g. PhD, MD) and deep field expertise, and who have demonstrated business acumen and analytical skills




![[Free] Afrinvest Assessment Past Questions Answers-PDF Download [Free] Afrinvest Assessment Past Questions Answers-PDF Download](https://teststreams.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/afr-2.jpg)
